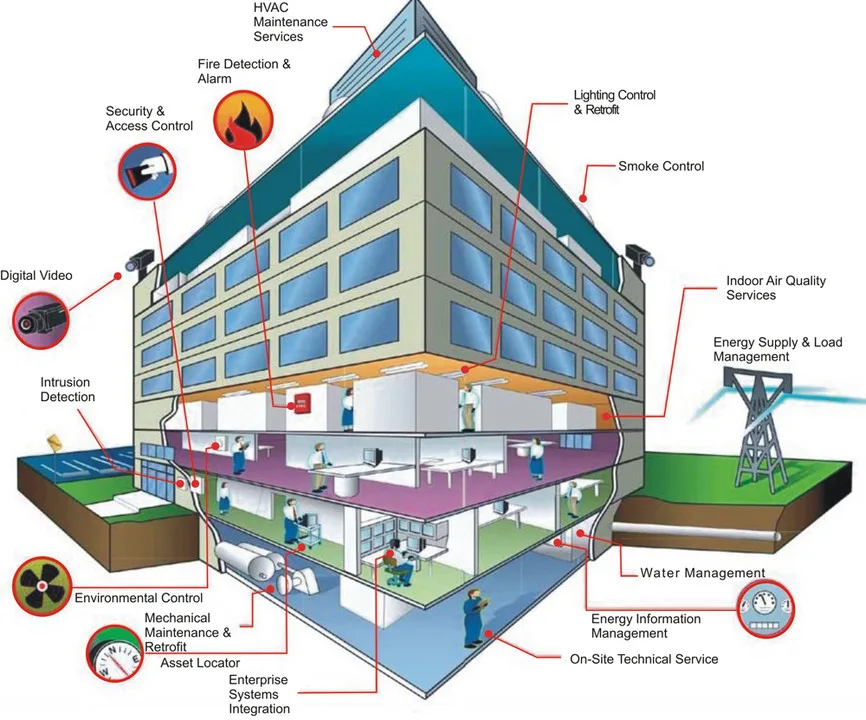
With the advancement of technology, automation has made life easier in various aspects, including building management. Building management companies are increasingly integrating intelligent automation systems into their infrastructures to provide sustainable solutions. A Building Management System (BMS) is a computer-based control system that manages and monitors a facility. Sensors in a building collect data and send it to the BMS, which stores it. If the data goes beyond set conditions, the system alerts the management. A BMS can monitor several key systems in a building, such as HVAC, Technical Steam, Dust Collection, Heat Blowers, Central Vacuum, Chilled/Hot Water, Sprinkler, and Electrical Monitoring systems.
Leading companies in building management systems include Cisco, Honeywell, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Bajaj Electrical, United Technologies, Emerson Electric, and Bosch. These companies offer services and solutions that help reduce costs and increase efficiency. In today’s high-inflation environment, modern technologies like BMS are essential in both offices and homes. The efficiency and cost-saving benefits of a BMS depend on the initial investment. With global energy consumption expected to rise by 50% by 2030, it is crucial to implement such systems. BMS can intelligently manage system demands, control electrical systems, heating and cooling, ventilation, plumbing, and fire alarms. Additionally, it can enhance safety and maintain a record of activities.
Understanding Building Management Systems (BMS)
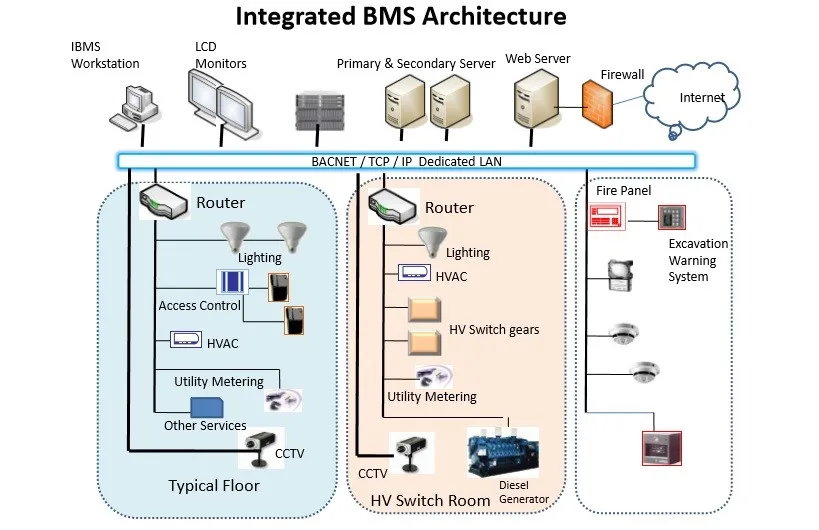
A BMS, also known as Building Automation Systems (BAS) or Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS), monitors and controls electrical and mechanical services within a building. This includes HVAC systems, lighting, security, access control, elevators, and safety systems. A BMS can be integrated into both new construction projects and existing buildings, offering a wide range of benefits.
Benefits of a BMS
Compared to separate control systems, a BMS offers centralized control, flexibility, interactivity, and feedback. It allows for comprehensive control and optimization of equipment cycles, focusing on energy efficiency. Energy-saving strategies such as accurate control of comfort conditions, precise start-up and run times, and economy cycles can be implemented with a BMS. Additionally, a BMS helps maintain tuning of HVAC systems, responding to drift in real time and flagging excessive energy use.
Reasons for Upgrading to a New BMS
A BMS older than 10 years is likely to benefit from an upgrade or replacement due to reliability issues, poor condition of components, lack of web compatibility, and difficulty in incorporating new equipment and sensors. Upgrading to a new BMS can result in lower maintenance costs, improved occupant comfort, and better performance management and reporting.
Innovations in BMS
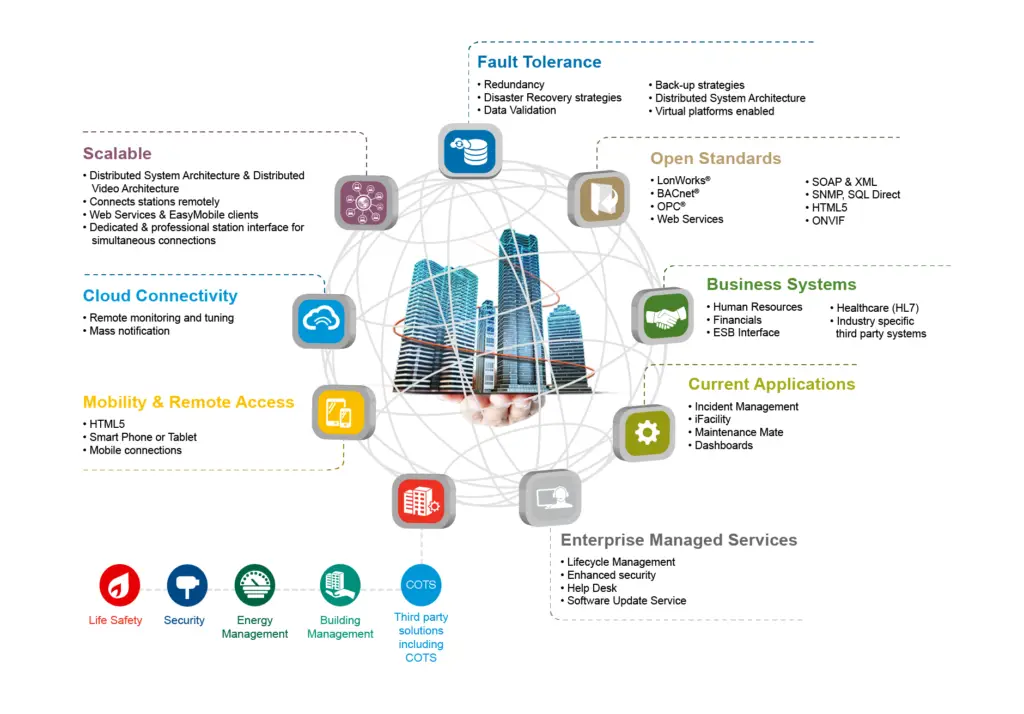
Recent innovations in BMS technology include a wider range of communication protocols, affordable wireless networks, and opportunities for grid-responsive demand management. BMS are increasingly being integrated with software-based, grid-responsive demand management systems, allowing for the optimization of energy consumption, generation, export, and storage. Predictive capabilities of BMS are also improving, allowing for more efficient energy use based on anticipated weather conditions and building loads.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Building Management Systems (BMS) are essential tools for optimizing the performance of commercial buildings. By providing centralized control and automation of various building systems, a BMS can significantly improve energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and operational efficiency. With continuous advancements in technology, BMS are becoming more sophisticated, offering a wide range of innovative features and benefits for building owners and operators.